Tansparent Connections: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Here is an example configuration of Transparent connections: | Here is an example configuration of Transparent connections: | ||
[[ | [[Image:Transparent.jpg]]<br /> | ||
There is a configuration for serial to TCP/IP transparent connection. (Serial-to-Ethernet converter).<br /> | There is a configuration for serial to TCP/IP transparent connection. (Serial-to-Ethernet converter).<br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:12, 4 June 2019
Transparent Connections is a feature to transfer raw data between two ports. Hence the term "transparent connection".
For example, transparent connections may be used as a serial-to-ethernet converter for devices with serial communication interface. This way, the device could be remotely configured via serial-to-ethernet connection.
Transparent connections enables transferring data in the following configurations:
- serial to serial
- serial to TCP/IP and TCP/IP to serial
- TCP/IP to TCP/IP (i.e port forwarding)
Here is an example configuration of Transparent connections:
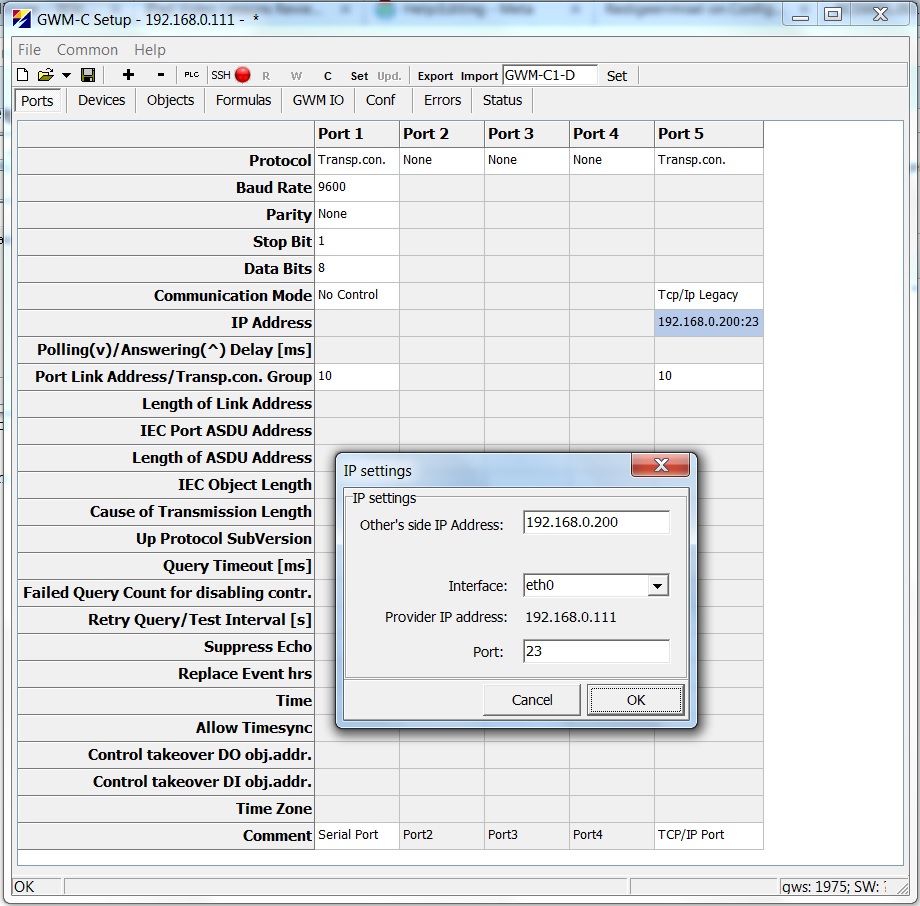
There is a configuration for serial to TCP/IP transparent connection. (Serial-to-Ethernet converter).
Port5 is configured as TCP/IP port of the transparent connection.
Note the parameter "Transp. con. group" (in this case, it is 10). This parameter is used to identify the two transparent ports that belong to the same connection group. If another pair of transparent connections is needed, create two more transparent ports and pair them together with the "Transp. con. group" parameter. Obviously, the second pair of transparent connections requires another value for the "Transp. con. group" parameter (in this case, some value other than 10).
Incoming TCP/IP connection is accepted from TCP port 23.
Access is limited to client IP 192.168.0.200
If this limitation is not needed, configure the "Other side address" as 0.0.0.0
In this example, all the data that is sent to server @ 192.168.0.111, tcp port 23 by client 192.168.0.200 is sent to serial line (Port1) @ 9600 baud, 8N1